Accurate and efficient laboratory billing for physicians plays an important role to ensure fair compensation for the diagnostic expertise. But keeping up with the ever-changing physician billing guidelines for laboratory services is challenging.
So, this guide will unpack the key components of a successful billing cycle for in-house laboratories from ensuring medical necessity documentation to bundling and unbundling tests to CPT coding accuracy for physician office lab billing.
Let us start with the basics of the lab billing landscape and slowly grasp the best practices to ensure smooth lab billing for physicians.
Can a Physician Own a Lab
Yes, a physician can own a lab as per a few exceptions into the Stark Law under certain conditions. But needless to say that they must comply with the law and other regulations to avoid any violation when operating an in-house laboratory.
Can a Physician Office Bill for Laboratory Services?
Yes, a physician office can bill for laboratory services only if it has an in-house certified laboratory. These in-house physician’s labs typically handle basic procedures like blood count and urinalysis. But in most cases, it’s the laboratory itself that bills the patient’s insurance for the tests they perform.
6 Major Types of Laboratories
When billing for laboratory tests as a physician order for your patients, the specific lab type can influence the process slightly. Let us share a quick rundown of 6 common lab types.
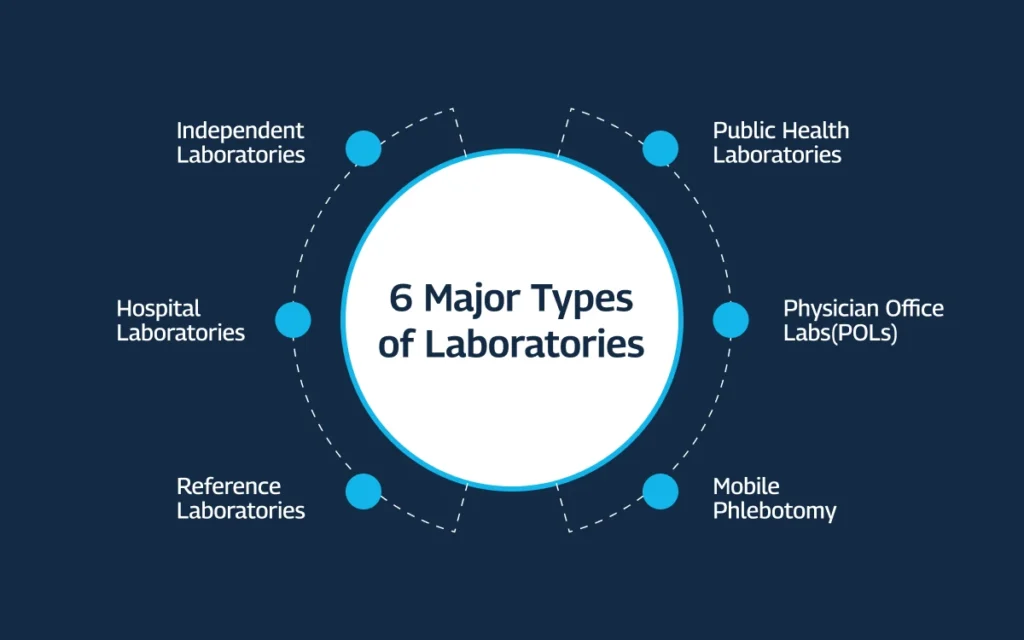
1. Independent Laboratories
The independent labs offer a wide range of tests and serve multiple healthcare providers. You, the physician, are responsible for billing the patient’s insurance company for any tests ordered from an independent lab.
2. Hospital Laboratories
If you work at a hospital and order tests for your in-house patients, the hospital billing system typically handles everything. However, if you’re a private practice physician admitting a patient to the hospital, you’ll still be responsible for billing any lab tests you order for them.
3. Reference Laboratories
The reference labs specialize in complex tests and act as a resource for advanced diagnostics. Billing for these tests also follows the same lab billing guidelines as any other lab test you order, which means, it falls on you, the physician.
4. Public Health Laboratories
Public health labs are responsible for public health concerns, including infectious disease surveillance, environmental testing, and emergency response. So, these labs don’t typically handle tests ordered by individual physicians like you.
5. Physician Office Laboratories (POLs)
These in-office labs allow for quick testing. Billing for POL tests is similar to billing for tests outsourced to any outside lab. And you’ll submit the claim to the relevant insurance company.
6. Mobile Phlebotomy Services
These services collect blood samples at convenient locations like a physician office or a hospital. Even though the blood draw happens outside your office, you’re still responsible for billing the insurance company for any tests ordered through them.
Now that you know the proper billing procedure for lab services depending on the type, let us discover the key players in the lab billing cycle.
3 Key Players in the Laboratory Billing Cycle for Physicians
Before we dive deeper into the physician billing guidelines for laboratory services, you must meet your success team to ensure proper medical billing for lab tests.
1. You (the Physician) for Medical Necessity Documentation
You play an important role by only ordering tests that are medically necessary for your patient’s diagnosis or treatment. Clearly documenting the reason for the test in the patient’s medical record is essential for getting reimbursed by insurance companies.
Remember that they may deny coverage for the outsourced tests they legally think are unnecessary.
2. Your Medical Billing Team for Coding Accuracy
Your billing team, either in-house or through a dedicated billing company, takes care of the technical aspects of submitting claims to insurance. We as your lab-specific billing partner at LBS use super accurate CPT codes for each test to ensure accurate coding.
Contact us right now to avoid claim denials or delays in receiving your rightful payment.
3. Payers And Their Coverage Policies
Insurance companies or payers determine what portion of the lab test cost they’ll cover for your patient. It’s important for you to be familiar with your patients’ insurance plans and the specific coverage policies for laboratory tests. Understanding the privileges helps avoid surprises for patients and ensures the tests you order are covered.
7 Essential Physician Billing Guidelines for Laboratory Services
Mastering the essential guidelines of physician billing for lab services helps optimize your revenue cycle as a physician, ensuring healthy financials for your office.

1. Ensure Medical Necessity
Medical necessity is a legal doctrine that mandates a healthcare activity like ordering for tests is extremely necessary based on solid reasons and clinical standards. It is the foundation of getting properly reimbursed. So, ensure a specific test is truly necessary for your patient’s care, justifying its financial responsibility.
Here’s How to Ensure Strong Medical Necessity Documentation:
You as a physician must clearly link the test to the diagnosis, document historical medical details, and use specific terminology to ensure solid medical necessity documentation.
a) Clearly Link the Test to the Diagnosis
Explain how the test result will help you diagnose or manage the patient’s condition. Don’t simply state “to rule out” a condition. Explain why the test is necessary based on the patient’s specific presentation and avoid vague justifications.
b) Document Relevant Medical History
Include details about the patient’s symptoms, past medical history, and current medications to establish why the test is necessary. Missing historical data is one of the common pitfalls to avoid in medical necessity documentation and can raise red flags for insurance companies, leading to denials.
c) Use Specific Terminology
Share the relevant clinical lab billing guidelines or research supporting the use of the test for your patient’s specific situation. Avoid copying and pasting generic justifications and tailor your documentation accordingly.
2. Ensure Precision in CPT Codes
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes act as the universal language for billing medical services, including laboratory tests outsourced by physicians. Accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement and avoids delays or denials for physician offices.
You can review your lab test requisition forms and comply with the latest physician office laboratory billing guidelines.
a) Review Your Lab Test Requisition Forms
These forms often include the corresponding CPT code for each test ordered. Double-check these codes to adhere to the proper physician billing guidelines for laboratory services.
b) Stay Informed About Billing and Coding Updates
Staying updated with the recent physician billing and coding guidelines for laboratory services ensures you align with the industry standards. It also mitigates the risk of coding-related claim denials.
These are the resources you must go through regularly to stay updated about the coding standards:
- ICD-10-CM Guidelines
- CPT Guidelines
- HCPCS Level II Guidelines
- CMS Internet-Only Manuals
- CMS Physician Fee Schedule
- NCCI (National Correct Coding Initiative) Policy Manual
- Regulatory Bodies like CMS and Private Payers
- Industry Associations like the AMA and ASCP
- Payer Specific Billing Guidelines
- Use other online coding resources like our LBS lab billing blog.
3. Append Proper Modifiers
While mastering CPT coding is crucial for physician billing for lab services, using proper laboratory modifiers helps ensure the accuracy and specificity to your claims. These modifiers are additional codes to provide more details about the services used, influencing reimbursement rates for you.
There are two major types or categories of laboratory modifiers:
1. Informational Modifiers
The informational modifiers convey details about the circumstances under which a test was performed. For example, Modifier 91 (Repeat Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Test) is used when a specific laboratory test needs to be repeated on the same date for the same patient to monitor treatment progress or due to indecisive initial results.
2. Pricing Modifiers
The pricing modifiers can impact the reimbursement rate for a laboratory test. But, it’s not as common as informational modifiers. For example, QW (CLIA-Waived Test) shows that a test was performed using a test kit approved by the CLIA for waived settings.
These tests usually need minimal training to perform and can be done in physician’s offices or other point-of-care facilities.
4. Properly Do the Bundling and Unbundling Tests
Properly implementing the bundling and unbundling in laboratory billing for physicians is important to optimize the billing cycle for you. Let’s quickly define what these terms mean and how to use them appropriately.
a) Bundling for Routine Tests
Bundling refers to grouping together related laboratory tests under a single CPT code for billing purposes. You implement bundling for standard tests that offer a comprehensive assessment of a specific body system or condition.
Grouping tests together reduces administrative burden for both physicians and billing teams. It also comes with a lower overall reimbursement rate compared to billing each test individually.
Examples of commonly bundled tests include CBC, CMP, and Lipid Panel.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
CMP evaluates various aspects of your blood cells, including RBCs, WBCs, and platelets.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
This test panel assesses your kidney function, electrolytes, liver function, and other metabolic processes.
Lipid Panel
Lipid Panel measures cholesterol levels and other fats in your blood.
b) Unbundling for Individual Tests
Bundling refers to grouping together related laboratory tests under a single CPT code for billing purposes. You implement bundling for standard tests that offer a comprehensive assessment of a specific body system or condition.
Unbundling refers to billing for individual tests within a bundled panel separately. It’s comparatively less common, but it’s still an appropriate part of physician billing guidelines for laboratory services.
- If you only need a specific test from a bundled panel for your patient’s diagnosis or treatment, you might choose to unbundle and bill for that single test.
- Some insurance companies might not cover bundled services, making unbundling necessary to ensure reimbursement for the test needed.
Unbundling helps increase your revenue and can be considered fraudulent billing. Insurance companies often scrutinize unbundled claims more closely. Unbundle only for medically necessary reasons. And ensure justification for unbundling based on medical necessity and implement proper documentation accordingly.
When Unbundling Might be Necessary
Unbundling involves billing for individual tests within a bundled panel separately. This might be appropriate if you only need a specific test from the panel or if the patient’s insurance plan doesn’t cover bundled services.
Note: Each insurance company might have specific policies regarding bundling and unbundling. Familiarize yourself with their rules to avoid denials. And consider outsourcing your physician’s lab billing services for accurate reimbursement while adhering to ethical billing practices.
5. Comply With the Relevant Healthcare Laws
Beyond accurate coding and documentation, physicians must uphold the best lab billing practices and comply with the relevant laws like The Stark Law, Anti-Kickback Statute, and The No Surprises Act when ordering and billing for laboratory services.
The Stark Law and Anti-Kickback Statute
These federal laws aim to prevent conflicts of interest, prohibiting physicians from referring patients to labs in which they have financial benefits like referral commissions.
The No Surprises Act
The recent legislation protects patients from unexpected medical bills, including those arising from out-of-network laboratory services. Physicians must be aware of the provisions of this act to ensure compliance.
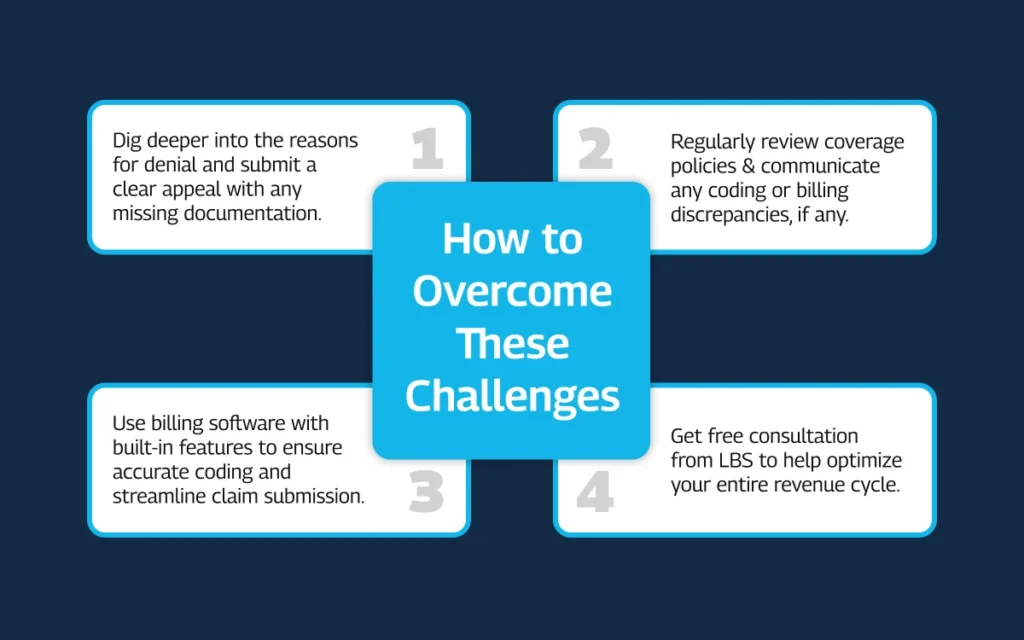
6. Overcome Reimbursement Challenges
Even after implementing these physician billing guidelines for laboratory services, labs and physicians may face many reimbursement challenges. These challenges can include denied claims, delayed payments, and slashed reimbursement rates.
Here’s how to overcome these challenges:
- Don’t accept denials passively. Understand the reason for denial and submit a clear and concise appeal with any missing documentation or justification.
- Regularly review coverage policies and communicate any coding or billing questions proactively.
- Consider using billing software with built-in features to ensure accurate coding and streamline claim submission, potentially reducing denials and delays.
- Get our free consultation to help optimize your entire revenue cycle.
7. Learn About the New Tech and Tests
The world of laboratory medicine is constantly evolving, with new tests and technologies emerging daily. Stay abreast of the impact of new laboratory tests like pharmacogenomics (focusing on gene-drug interactions) and liquid biopsies (detecting cancers through blood tests).
Billing for these new tests might not be straightforward. But the good news is that our certified physician lab billers and coders stay informed about new tests and their associated CPT codes so you always stay healthy in finances.
Optimize Physician’s Billing Success
While this guide to physician billing guidelines for laboratory services equips you with a strong foundation, consider partnering with lab billing services to further streamline your laboratory billing processes. We specialize in optimizing laboratory billing for physicians and offer these valuable services:
- Expert coding and claim submission
- Insurance verification and pre-authorization
- Denial management and appeals processing
- Regulatory compliance guidance
- Integration with your existing practice management system.
Partnering with lab billing services can free up valuable time and resources within your practice, allowing you to focus on patient care. Get a FREE evaluation session to help you optimize billing revenue for your laboratory.

